
Disk Utility User Guide
Disk Utility is free and included with every copy of the Mac OS. And while the various cloning apps have a lot more features, if you don’t have access to third-party apps, using Disk Utility will create a perfectly usable clone, although it may require a few more steps and lacks some nice features, such as automation and scheduling. Disk Utility can find and repair errors related to the formatting and directory structure of a Mac disk. Errors can lead to unexpected behaviour when you're using your Mac, and significant errors may even prevent your Mac from starting up completely. Apple: MacBook Pro disk utility - disk0s2 not mountedHelpful? Please support me on Patreon: thanks & praise to God.
Let macOS manage space between multiple volumes
With Apple File System (APFS), the file system introduced in macOS 10.13, you can easily add and delete volumes on your storage devices. APFS-formatted volumes automatically grow and shrink—you never have to repartition a storage device again.
Keep your external storage devices secure
When you get a new flash drive or other storage device, format it as APFS and encrypt it with a password to protect its contents.
- Use Disk Utility to erase your Mac Start up from macOS Recovery: Turn on your Mac, then immediately press and hold these two keys until you see an Apple logo or other image: Command (⌘) and R. If asked, select a user you know the password for, then enter their administrator password.
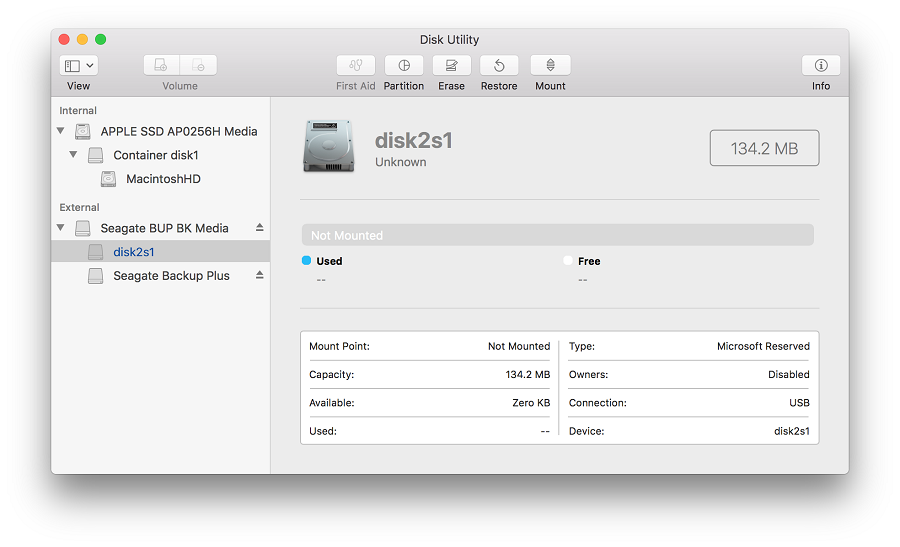
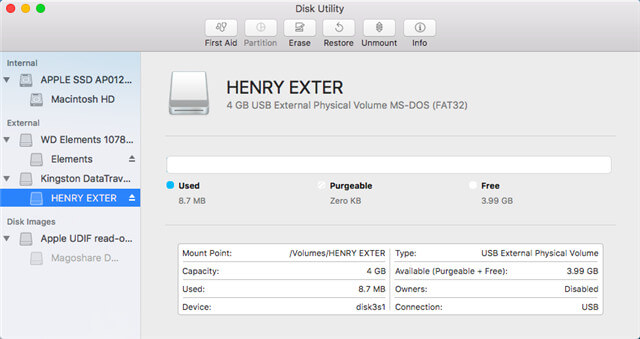
- Partition schemes available in Disk Utility on Mac. Get detailed information about a disk. Manage physical disks and volumes. Add, erase, or delete APFS volumes. Erase and reformat a storage device. Encrypt and protect a storage device with a password. Partition a physical disk.
Give your disk a checkup
If you’re having problems with a disk, Disk Utility can check the disk and repair problems it detects.
To explore the Disk Utility User Guide, click Table of Contents at the top of the page, or enter a word or phrase in the search field.
| Operating system | macOS |
|---|---|
| Type | Utility |
| Website | support.apple.com/guide/disk-utility/welcome/mac |
Disk Utility is a system utility for performing disk and disk volume-related tasks on the macOSoperating system by Apple Inc.
Functions[edit]
The functions currently supported by Disk Utility include:[1]
- Creation, conversion, backup, compression, and encryption of logical volume images from a wide range of formats read by Disk Utility to .dmg or, for CD/DVD images, .cdr
- Mounting, unmounting and ejecting disk volumes (including both hard disks, removable media, and disk volume images)
- Enabling or disabling journaling
- Verifying a disk's integrity, and repairing it if the disk is damaged (this will work for both Mac compatible format partitions and for FAT32 partitions with Microsoft Windows installed)
- Erasing, formatting, partitioning,[2] and cloning disks
- Secure deletion of free space or disk using a 'zero out' data, a 7-pass DOD 5220-22 M standard, or a 35-pass Gutmann algorithm
- Adding or changing partition table between Apple Partition Map, GUID Partition Table, and master boot record (MBR)
- Restoring volumes from Apple Software Restore (ASR) images
- Checking the S.M.A.R.T. status of a hard disk
Disk Utility functions may also be accessed from the macOS command line with the diskutil and hdiutil commands.[3]
History[edit]
Disk Utility Mac Erase Greyed Out
In the classic Mac OS, similar functionality to the verification features of Disk Utility could be found in the Disk First Aid application. Another application called Drive Setup was used for drive formatting and partitioning and the application Disk Copy was used for working with disk images.
Before Mac OS X Panther, the functionality of Disk Utility was spread across two applications: Disk Copy and Disk Utility. Disk Copy was used for creating and mounting disk image files whereas Disk Utility was used for formatting, partitioning, verifying, and repairing file structures. The ability to 'zero' all data (multi-pass formatting) on a disk was not added until Mac OS X 10.2.3.[4] Further changes introduced in Mac OS X Tiger, specifically version 10.4.3, allowed Disk Utility to be used to verify the file structure of the current boot drive. Mac OS X Leopard added the ability to create, resize, and delete disk partitions without erasing them, a feature known as live partitioning. In OS X El Capitan, Disk Utility has a different user interface and lost the abilities to repair permissions due to obsolescence,[5] create and manage disks formatted as RAID, burn discs, and multi-pass format internal solid-state drives and encrypted external drives.[6]
See also[edit]
Disk Utility Mac Ntfs
References[edit]
- ^'Disk Utility 10.5 Help: Testing and repairing a disk or volume'. Apple Inc.
- ^'Mac OS X 10.5: About resizing disk partitions'. Apple Inc.
- ^Landau, Ted; Frakes, Dan (December 20, 2005). Mac OS X Help Line, Tiger Edition. Peachpit Press. ISBN9780132705240.
- ^'Mac OS X: About the Mac OS X 10.2.3 Update'Archived March 27, 2008, at the Wayback Machine. Apple Inc.
- ^'OS X v10.11 Developer Beta 7 Release Notes'. Mac Developer Library. Apple Inc. August 18, 2015. Retrieved October 7, 2015.[permanent dead link]
- ^Cunningham, Andrew; Hutchinson, Lee (September 29, 2015). 'OS X 10.11 El Capitan: The Ars Technica Review'. Ars Technica. Retrieved September 30, 2015.